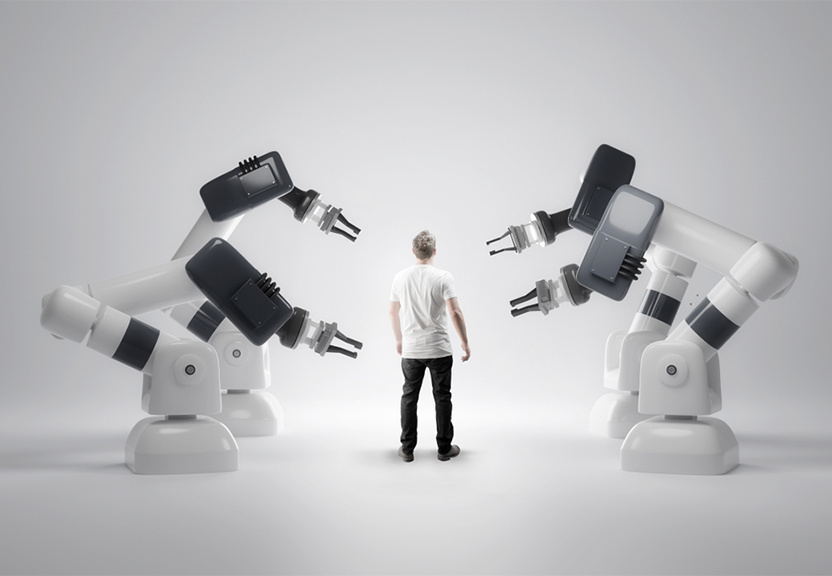
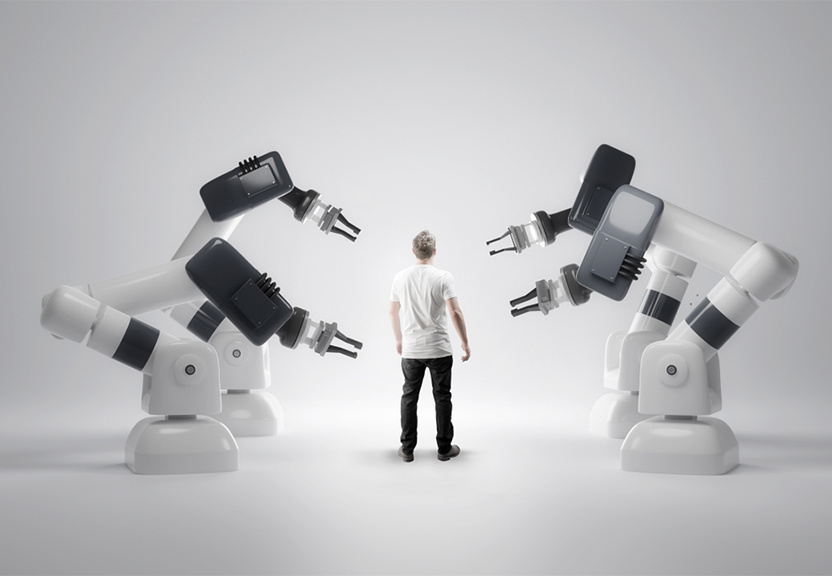
The Impact Of Automation On The Workforce And Job Market
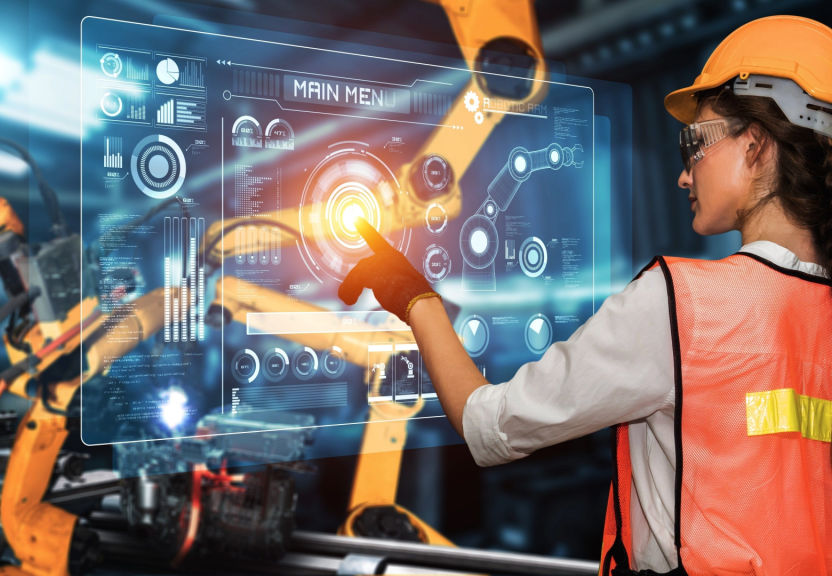
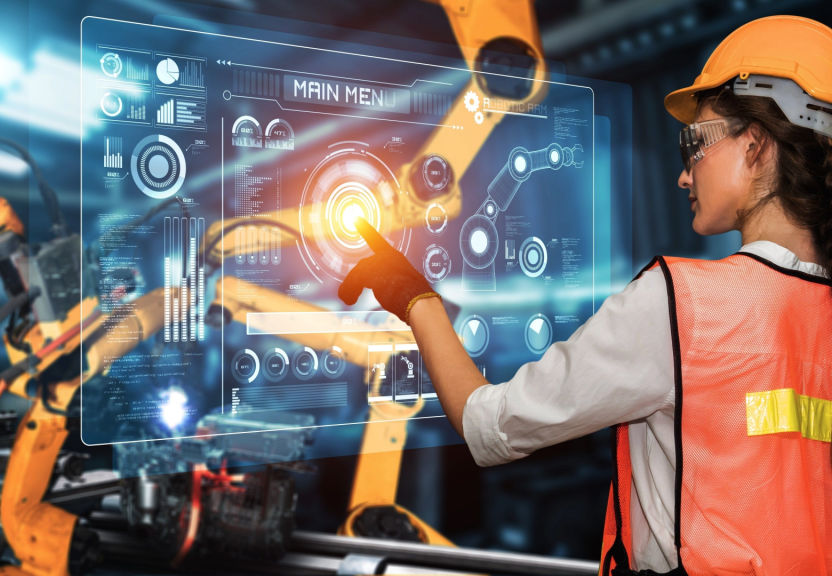
Automation, driven by advances in technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Robotics, is rapidly changing the way we work and the way we think about the workforce and job market. Automation has the ability to perform tasks that were previously done by humans, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. However, it also has the potential to displace jobs and change the way we think about work. In this article, we will explore the impact of automation on the workforce and job market and the potential benefits and challenges of this technology.
One of the most significant potential impacts of automation on the workforce is the displacement of jobs. Automation has the potential to automate repetitive, routine and dangerous tasks, leading to job losses in sectors such as manufacturing and transportation. However, it’s important to note that the displacement of jobs doesn’t necessarily mean job loss, as automation can also lead to the creation of new jobs in fields such as data analysis and AI development.
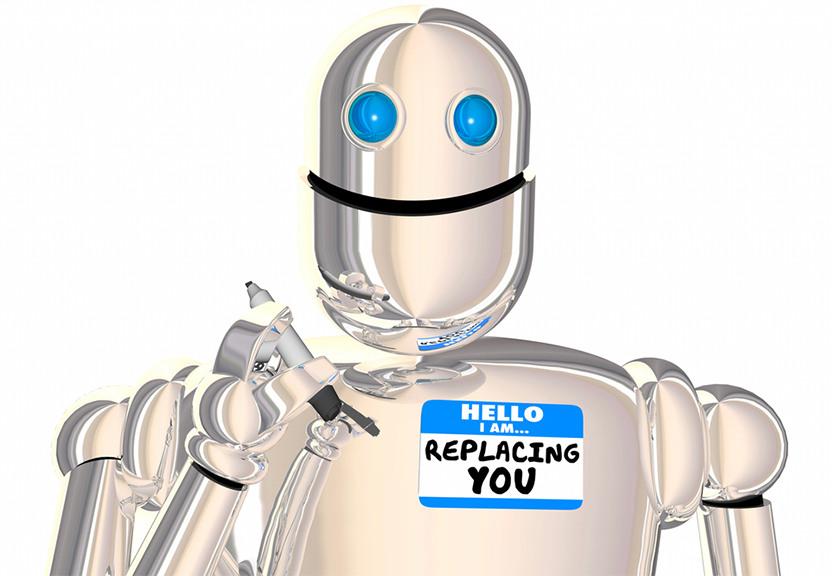
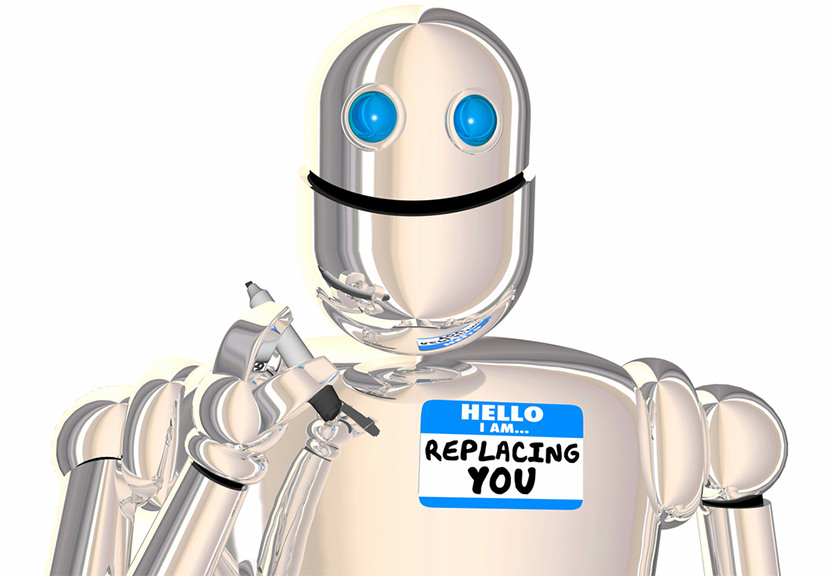
Another potential impact of automation on the workforce is the change in the nature of work. Automation can lead to the redistribution of tasks between humans and machines, making some tasks more complex and others more simple. This could lead to the need for new skills, such as data analysis and AI development, as well as the need for reskilling and upskilling of existing workers.
Automation also has the potential to improve working conditions and increase productivity by reducing the need for humans to perform repetitive, routine, and dangerous tasks. This could lead to improvements in safety, as well as increased efficiency and productivity, which can have a positive impact on the economy.
Despite these benefits, there are also challenges to the impact of automation on the workforce and job market. One major challenge is ensuring that the benefits of automation are distributed fairly, particularly in terms of ensuring that workers who are displaced by automation have access to new job opportunities and training programs. Additionally, there is a need for a comprehensive social safety net to support workers who are displaced by automation. Furthermore, there is a risk that automation could lead to increased income inequality, as higher-skilled jobs may become more valuable and better-paid, while lower-skilled jobs may become less valuable and lower-paid.
In conclusion, automation is rapidly changing the way we work and the way we think about the workforce and job market. It has the potential to increase efficiency and productivity, as well as the creation of new job opportunities in fields such as data analysis and AI development. However, it also has the potential to displace jobs and change the nature of work. To ensure that the benefits of automation are distributed fairly, it is important to invest in education and training programs to prepare workers for a future where automation is prevalent, and to provide a comprehensive social safety net to support workers who are displaced by automation. Additionally, policies and regulations should be implemented to address the potential negative impacts of automation such as income inequality and lack of access to new job opportunities. It is crucial that we approach the integration of automation in the workforce and job market with a holistic and forward-thinking perspective to ensure a fair and prosperous future for all.
The articles and information within this website are my sole opinion and derived from my sole experience. They are meant for general information purposes only and is not meant to substitute professional dietary and/or health advice or treatment. If you have or suspect you may have allergies or medical issues which may be affected by certain foods, or have or suspect you may have any illness and/or disease and/or chronic ailment and/or other, you should promptly contact your health care provider. Any statements regarding diets and/or nutrition and/or health are to be used at your discretion and are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.